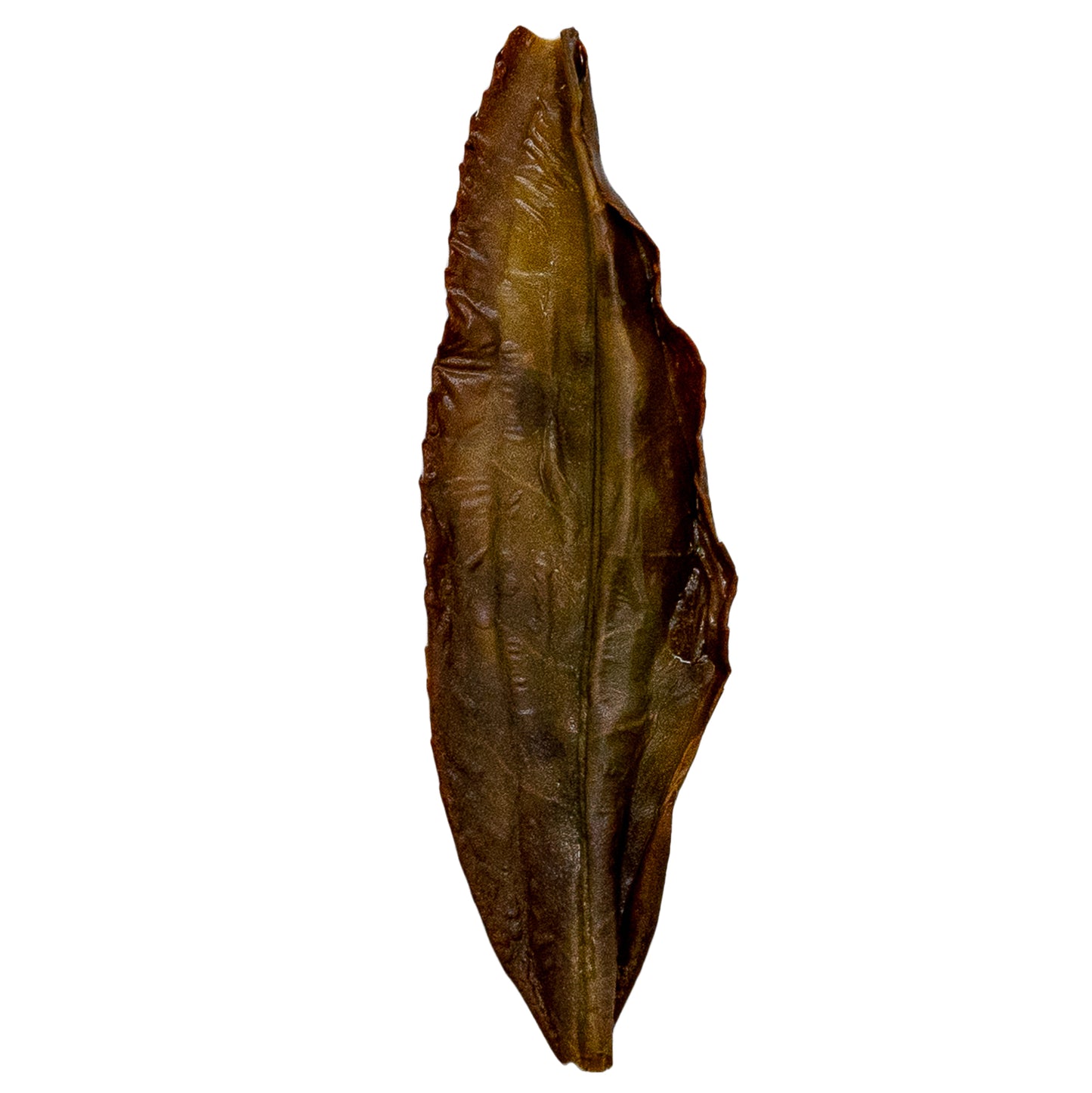
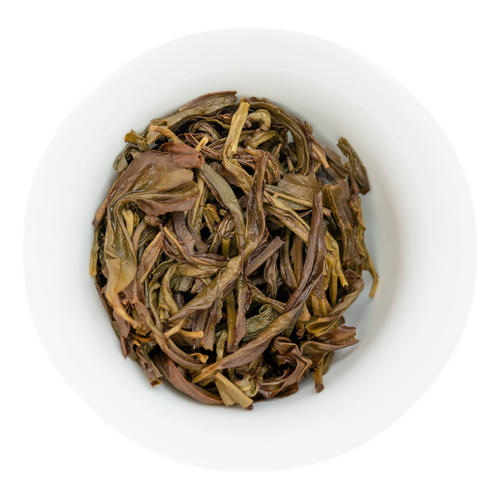
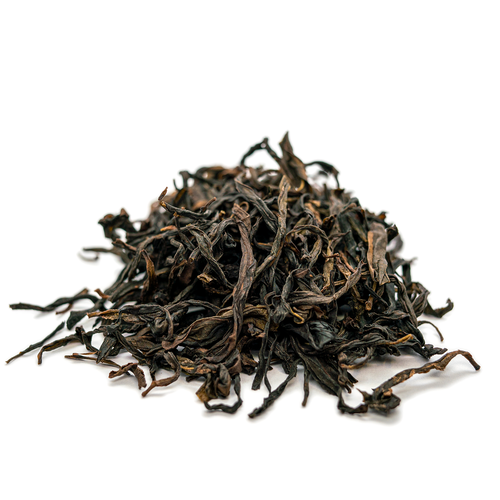
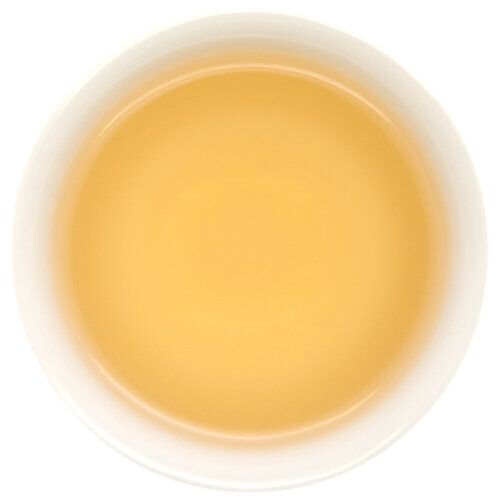
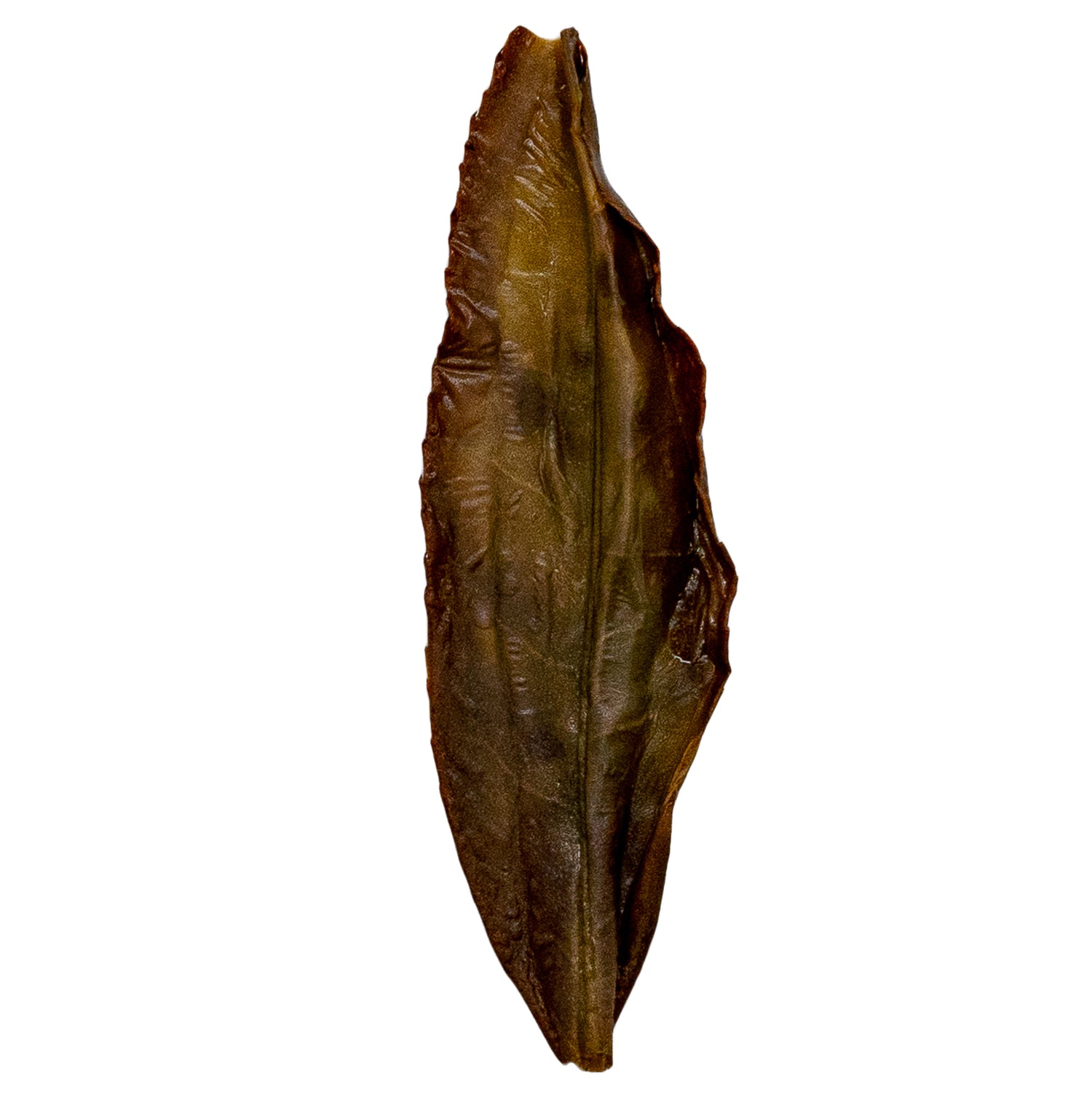
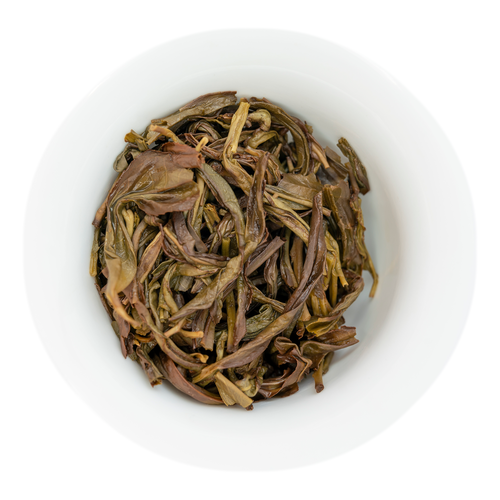
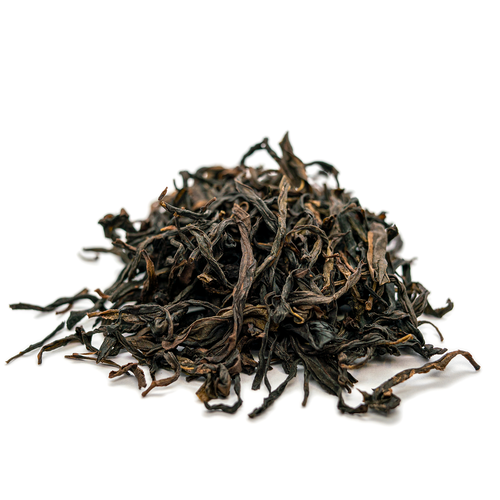
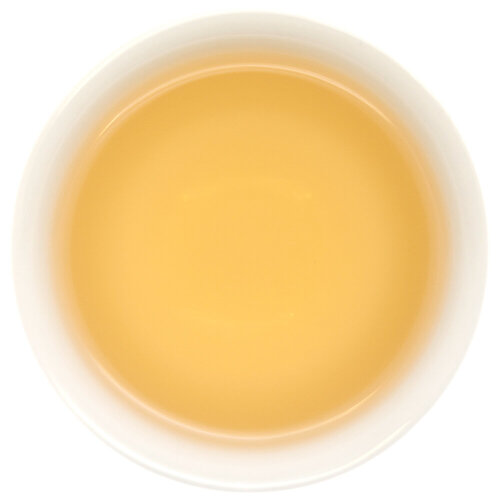
Bai Ye is best known for its very forward fruity peach notes. Our varietals come from some of the highest sought-after terroirs for Dan Cong Wu Long.
Bai Ye has a high yield, buds early, and is easy to make with reliable outcomes. The delightful peachy notes also make it one of the most popular teas on the market. However, Bai Ye is often mistakenly sold as Mi Lan Xiang (honey orchid) but is a more economical varietal. This tea is also not the same as a varietal called Da Bai Ye.
Refreshing & tannic with prominent notes of peach and lychee. This tea has a signature yolky aftertaste.
The freshly picked leaves need to be sun wilted first. Once the leaves are silky and soft, they are moved inside to continue to wilt under shade and gently flipped occasionally. The shaking step is the signature step to making Wu Long (Oolong), where the tea maker shows their skill by regulating how the water travels from the stems to the leaves and out. It is traditionally done by shaking the leaves on a bamboo tray but is now commonly done with a tumbling machine. This step varies by tea and by the weather; it takes a thoroughly experienced tea maker to decide how soon and often to shake the tea. This step usually takes tea makers all night to complete. After the tea has rested for a few hours to ferment, the leaves are then transferred to a firing wok or machine to have all the residual enzymes killed early in the morning. The hot teas are then transferred to a rolling device, rolled into string shapes, and spread out evenly onto baking trays to be baked dry. After the tea season, the refining process of tea making starts with the tedious step of picking out old stems and leaves, usually taking months to finish. Then the “cleaned” teas are charcoal roasted over a very dim ash fire for 6-10 hours. Many teas need to repeat this step, with at least three weeks' resting time between each roasting.